RSA 소개 및 개인키 로직 포스트: https://shacoding.com/2019/07/28/rsa-find-d-using-ne-c/
암호화 인식 & 복호화 구현 문자
영어 소문자, 대문자, 숫자, 띄어쓰기, 특수문자(콤마, 점, 콜론, 세미콜론,소괄호, 느낌표, 물음표, 퍼센트, 대시, 큰 따옴표, 작은 따옴표) 구현
– 미구현 문자는 띄어쓰기 처리, 줄 바꿈 구현 불가
구현된 기능
1. 암호화 시 (영문 소문자, 대문자, 숫자, 특수문자) 인식 가능
2. 복호화 시 (영문 소문자, 대문자, 숫자, 특수문자) 구현 가능
3. 원 문자열 ->원 숫자 집합으로 분할 가능
4. 원 숫자 집합 -> 암호 숫자 집합으로 변경 가능 (암호화)
5. 암호 숫자 집합 -> 원 숫자 집합으로 변경 가능 (복호화)
6. 원 숫자 집합 -> 원 문자열로 통합 가능
7. 위 (1~6)의 코드 -> 프로시저화 완료
스크린샷으로 살펴보기

1.5. 원 문자열 -> 분할 -> 원 숫자 집합 생성




C언어 소스
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 2000
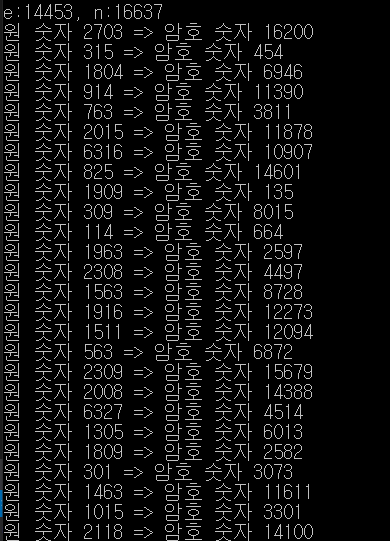
#define n 16637 // 공개 키 < (0 <= M <=n-1)에 주의해서 설정, 현재 M의 최대값은 7575 >
#define e 14453 // 공개 키
#define d 17 // 개인 키
/*
- 리스트 포인터 소개 -
* code = RSA 전처리 코드 집합 저장 (ex) a는 1로, b는 2로)
* bundle = 원 숫자 집합 저장 (ex) 102,203,1020,...)
* encode = 암호 숫자 집합 저장 (ex) 2120,3366, ...)
* decode = 복호화 숫자(원 숫자) 집합 저장 (ex) 102,203,1020,...)
*/
typedef struct list { // 리스트 구조체
int size;
int* array;
}list;
list* code, * bundle, * encode, * decode; // 여기서 선언하지 않으면 '댕글링 포인터'가 되어 버림
/*
- 함수 소개 (작업 실행 순서대로) -
* init() = RSA 작업에 필요한 리스트 생성 (code,bundle,encode,decode 리스트)
* get_symbol(char* tmp) = string의 문자열을 조각으로 나눠서 리턴 (ex) ab-> 'a','b')
* make_Code(char* string,list* code) = 문자 조각으로 전처리 코드 집합 생성 <code> (ex) a->1, b->2)
* get_integer(list* code) = 전처리 코드 2개로 원 숫자 만들기 (ex) 1,2 -> 102)
* make_Bundle(list * code,list* bundle) = 원 숫자 집합 생성 <bundle> (ex) 102,1021,1200,..)
* make_C(int M) = RSA 암호화 <원 숫자 -> 암호 숫자로 변경> (ex) 102 -> 3366)
* make_Encode(list *bundle,list *encode) = 암호 숫자 집합 생성 <encode> (ex) 3366,3450,9800,..)
* make_M(int C) = RSA 복호화 <암호 숫자 -> 원 숫자로 변경> (ex) 3366 -> 102)
* make_Decode(list* encode, list* decode) = 복호 숫자(원 숫자) 집합 생성 <decode> (ex) 102,1021,1200,..)
* get_Code(list* decode) = 복호 숫자(원 숫자) 분할해서 전처리 코드 반환 (ex) 102 -> 1과 2 반환)
* decode_Effect(list* decode) = RSA 전처리 코드를 아스키코드로 변환 후 문자 출력
↑(전처리 코드를 다 쓸때까지 반복) (ex) 1->97->'a'출력, 2->98->'b'출력, ...)
*/
void init();
char get_symbol(char* tmp);
void make_Code(char* string, list* code);
int get_integer(list* code);
void make_Bundle(list* code, list* bundle);
int make_C(int M);
void make_Encode(list* bundle, list* encode);
int make_M(int C);
void make_Decode(list* encode, list* decode);
int* get_Code(list* decode);
void decode_Effect(int* decode);
/* 아래는 (문자열 처리)에 필요함 */
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------------ */
// 원문자열 저장
char string[MAX] = "";
// 특수문자 배열
char sign[14] = { ' ',',','.',';',':','(',')','!','?','%','"',39,'-' }; // 39 = `
// 특수문자와의 거리
int sign_distance[14] = { 63 - 32,64 - 44,65 - 46,66 - 59,67 - 58,68 - 40,69 - 41,70 - 33,71 - 63,72 - 37,73 - 34,74 - 39,75 - 45 };
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------------ */
// 메인 함수
int main() {
init(); // RSA 작업에 필요한 리스트 생성
printf("■ 암호화할 문장을 적어 주세요:\n\n");
gets(string);// 원 문자열 입력해서 문자형 배열(string)에 저장(ex)string배열에 'abdcdi' 저장)
/* 암호화 과정 */
make_Code(string, code); // 전처리 코드 집합 생성
make_Bundle(code, bundle); // 원 숫자 집합 생성
make_Encode(bundle, encode); // 암호 숫자 집합 생성
/* 복호화 과정 */
make_Decode(encode, decode); // 복호 숫자(원 숫자) 집합 생성
printf("\n■ 다음과 같이 복호화되었습니다:\n\n");
decode_Effect(decode); // 복호 숫자 이용 -> 문자 출력까지
}
// RSA 작업에 필요한 리스트 생성
void init() {
// RSA 전처리 코드 저장 리스트
code = (list*)malloc(sizeof(list));
code->size = 0;
code->array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX);
// 원 숫자 집합(숫자 묶음) 저장 리스트
bundle = (list*)malloc(sizeof(list));
bundle->size = 0;
bundle->array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX);
// 암호화 코드 저장 리스트
encode = (list*)malloc(sizeof(list));
encode->size = 0;
encode->array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX);
// 복호화 코드 저장 리스트
decode = (list*)malloc(sizeof(list));
decode->size = 0;
decode->array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * MAX);
}
// string의 문자열을 조각으로 나눠서 리턴 (ex) ab-> 'a','b')
char get_symbol(char* tmp) {
static int j = 0;
return tmp[j++];
}
// 문자 조각으로 RSA 전처리 코드 저장 (ex) a->1, b->2)
void make_Code(char* string, list* code) {
char piece; // 문자 조각
// RSA 전처리 코드 저장
while ((piece = get_symbol(string)) != 0) {
// 영어 소문자 (a~z)
// RSA 전처리 시 -> 1~26으로 지정
if (piece >= 97 && piece <= 122) {
code->array[code->size] = piece - 96;
code->size++;
}
// 영어 대문자(A~Z)
// RSA 전처리 시 -> 27~52으로 지정
else if (piece >= 65 && piece <= 90) {
code->array[code->size] = piece - 38;
code->size++;
}
// 숫자 (0~9)
// RSA 전처리 시 -> 53~62으로 지정
else if (piece >= 48 && piece <= 57) {
code->array[code->size] = piece + 5;
code->size++;
}
// 특수 문자
// RSA 전처리 시 -> 63~73로 지정
else {
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++) {
if (piece == sign[i]) {
code->array[code->size] = i + 63;
break;
}
else if (i == 12)
code->array[code->size] = 63; // 없으면 공백 문자
}
code->size++;
}
}
}
// 전처리 코드 2개로 원 숫자 만들기
// ex) ab(12)가 오면 (a*100+b)를 반환, c(3)만 오면 c*100을 반환
int get_integer(list* code) {
static int i = 0;
// i가 리스트의 최고 idx보다 높을 때
if (i >= code->size) {
return -1;
}
// 마지막 원소를 다룰 때 (문자 개수는 홀수)
// ex) size=17, i=16
else if (i == code->size - 1)
return code->array[i++] * 100;
// 일반적인 것을 다룰 때
// ex) size=17, i=5; size=17; i=15;
else {
int first = code->array[i] * 100;
int second = code->array[i + 1];
i += 2;
return first + second;
}
}
// 원 숫자 집합(bundle) 생성 (ex) 102,1021,1200,..)
void make_Bundle(list* code, list* bundle) {
int receive;
while ((receive = get_integer(code)) != -1) {
bundle->array[bundle->size++] = receive;
}
}
// RSA 암호화 C = M^e mod n
int make_C(int M) {
unsigned long long C = 1; // 곱하기 하면서 오버플로우 될 수 있으므로 크게 설정
for (int i = 0; i < e; i++) {
C *= M;
C %= n;
}
return C; // 최종 나머지 값은 int형으로 해결 가능
}
// 암호 숫자 집합 생성 (ex) 3366,3450,9800,..)
void make_Encode(list* bundle, list* encode) {
printf("\ne:%d, n:%d\n", e, n);
for (int i = 0; i < bundle->size; i++) {
int M = bundle->array[i];
encode->array[encode->size] = make_C(M); // C = M^e mod n
printf("원 숫자 %d => 암호 숫자 %d\n", M, encode->array[encode->size]);
encode->size++;
}
}
// RSA 복호화 M = C^d mod n
int make_M(int C) {
unsigned long long M = 1; // 곱하기 하면서 오버플로우 될 수 있으므로 크게 설정
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
M *= C;
M %= n;
}
return M; // 최종 나머지 값은 int형으로 해결 가능
}
// 복호 숫자(원 숫자) 집합 생성(ex) 102, 1021, 1200, ..)
void make_Decode(list* encode, list* decode) {
printf("\n\nd:%d, n:%d\n", d, n);
for (int i = 0; i < encode->size; i++) {
int C = encode->array[i];
decode->array[decode->size] = make_M(C); // M = C^d mod n
printf("암호 숫자 %d => 원 숫자 %d\n", C, decode->array[decode->size]);
decode->size++;
}
}
// 복호 숫자(원 숫자) 분할해서 전처리 코드 반환 (ex) 102-> 1과 2)
int* get_Code(list* decode) {
static int z = 0; // idx역할
static int tmp[2]; // 정적 처리 -> 리턴해도 스택에서 안 사라지게
tmp[0] = tmp[1] = 0; // 값 매번 0으로 초기화
// z가 리스트의 최고 idx보다 높을 때
if (z >= decode->size) {
return -1;
}
// 마지막 원소를 다룰 때
// ex) 1819 1920 2100따위일 때 2100
else if (decode->array[z] % 100 == 0) {
tmp[0] = decode->array[z++] / 100;
}
// 일반적인 원소를 다룰 때
else {
tmp[0] = decode->array[z] / 100;
tmp[1] = decode->array[z] % 100;
z++;
}
return tmp;
}
/* RSA 전처리 코드를 아스키코드로 변환 후 문자 출력
↑(전처리 코드를 다 쓸때까지 반복) (ex) 1->97->'a'출력, 2->98->'b'출력, ...) */
void decode_Effect(int* decode) {
int* receive; // 전처리 코드의 주소를 저장
int get = 0; // receive[0]과 receive[1]이 저장됨
// get_Code 이용해서 전처리 코드 반환, 전처리 코드 모두 받을 때까지 문자 출력
while ((receive = get_Code(decode)) != -1) {
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
get = receive[i];
if (get != 0) {
// 영어 소문자
if (get >= 1 && get <= 26)
printf("%c", get + 96);
// 영어 대문자
else if (get >= 27 && get <= 52)
printf("%c", get + 38);
// 숫자
else if (get >= 53 && get <= 62)
printf("%c", get - 5);
// 특수문자
else {
for (int i = 0; i < 13; i++) {
// 넘어온 문자-특수문자와의 거리=특수문자일 때
// ex) 63-29=32(' ')
if (get - sign_distance[i] == sign[i]) {
printf("%c", sign[i]);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
프로그램 그림 설명

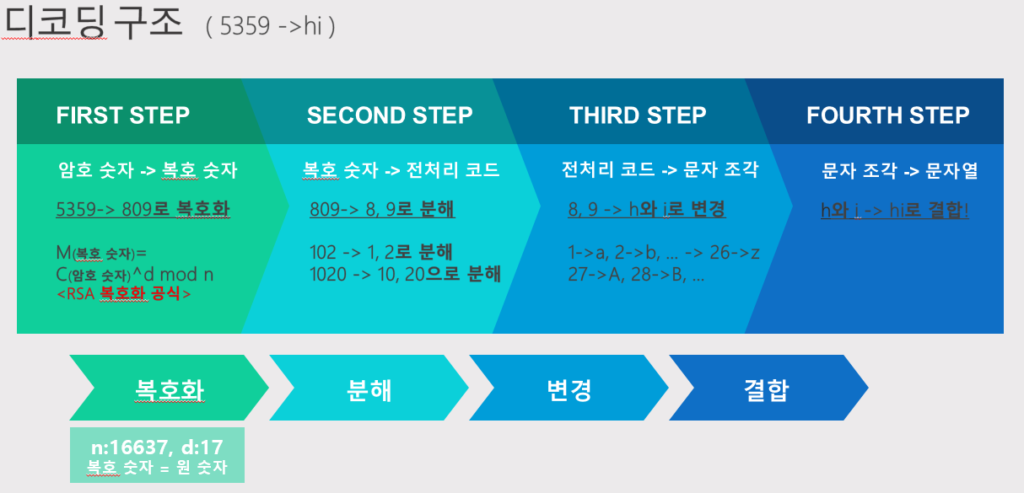

참고 자료: Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications (케네스 H. 로젠의 책)
